During Moderate Activity Which Fuel Sorce Is Used the Most
Both anaerobic and aerobic metabolism combine during exercise to ensure that the muscles are equipped with enough ATP to carry out the demands placed on them. Produces ATP in rather large quantities from other energy sources in the body.
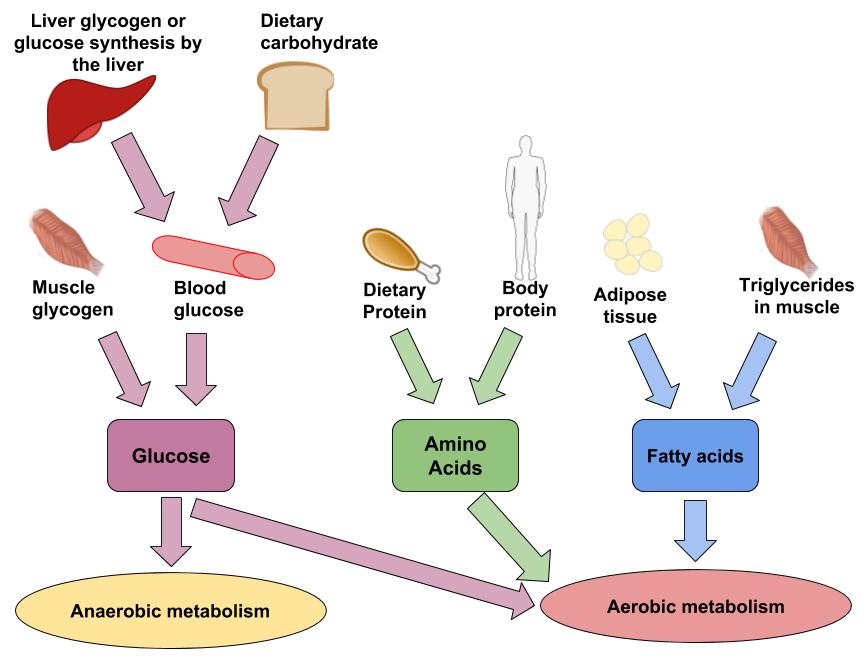
A Liver glycogen b Muscle glycogen c Intramuscular lipid d Adipose tissue lipid Question 6 Endurance type.
. Low-intensity exercise is around 40 to 50 percent of your maximum heart rate. Fat and carbohydrate CHO are the main fuels for aerobic metabolism during exercise in a well-fed person. This means there is indeed an exercise intensity where fat is the predominant energy source.
Fat oxidation cannot substitute. During strenuous exercise there is an obligatory demand for carbohydrate CHO oxidation that must be met. In the absence of oxygen your body can also use a carbohydrate source called glycogen to quickly produce ATP.
Moderate-intensity exercise is around 50 to. The type of substrate fuel and the rate at which it is utilized during exercise is largely dependent on the intensity and duration of the exercise. In contrast there is an increase in fat oxidation during prolonged moderate intensity exercise as.
High-intensity aerobics refers to any exercise method that can achieve and sustain a heart rate of 70 to 85 percent or more of your maximum heart rate. Aids endurance by sparing glycogen reservesGenerally as the duration or time spent exercising increases intensity decreases and more oxygen is available to cells and fat is the more. See Table 1 In contrast protein is not a preferred source of energy during any form of exercise assuming an adequate diet and generally contributes less than 10 percent of the total energy requirements.
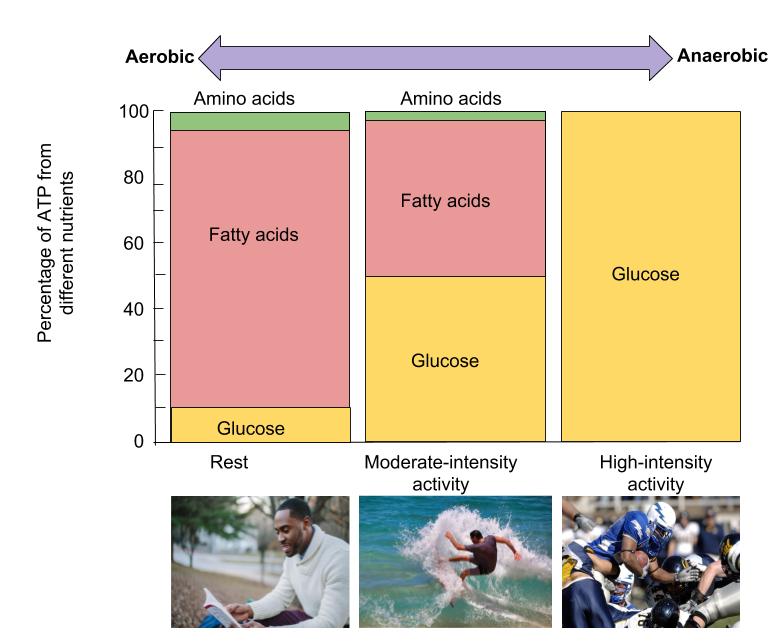
Carbs used during high-intensity exercise are from. As there is a limit to the amount of carbohydrate that can be stored in the muscles high-intensity work can only be sustained for short periods. What is the predominant fuel used by muscle cells during low or moderate intensity activity for multiple hours In prolonged activities where intensity is low the body will use fat as a main energy source and spare the use of muscle glycogen and blood glucose so that it is available for use if exercise intensity increases and oxygen availability is decreased.
At similar higher VO2 max levels of exercise arm exercise uses relatively more carbohydrate than leg exercise. Question 5 What endogenous substrate source provides the most energy during moderate to high intensity exercise. Fat is the primary energy source during.
Depends upon reactions that occur in the nucleus of the cell. What is the immediate source of chemical energy that can be used by skeletal muscle tissue to allow muscle contraction. The contribution from fat decreases at higher power outputs as CHO.
Blood glucose and stored glycogen in muscle and liver. The oxygen system _________. At low levels of exercise intensity most energy is supplied from fats in the bloodstream.
For very intense exercise in the anaerobic zone your body uses a high-energy compound called creatine phosphate which it breaks down into adenosine triphosphate or ATP -- the main unit of energy in all your cells. There is a limit to your carbohydrate storage so this energy system doesnt last long. Unless youre an elite endurance athlete most people can sustain a.
So the body will use carbohydrates as these can be metabolised more rapidly. Is used primarily in sports that demand strenuous exercise. Carbohydrates are easily changed into fuel and are the most immediate energy source your body has.
During low intensity exercise glycogen breakdown and thus glycolysis is not markedly stimulated so the increased availability of fatty acids allows their oxidation to serve as the predominant energy source. Although protein is not considered a major energy source small amounts of amino acids are used while resting or doing an activity. Primary Source of Energy During a High Intensity Aerobic Activity.
At higher intensity exercise stimulation of glycogen breakdown and glycolysis cause increased pyruvate entry into the TCA cycle for oxidation and as a consequence the. The first metabolic pathways of carbohydrate metabolism to be involved are skeletal muscle glycogenolysis and glycolysis. The two main sources of energy during muscular exercise are fat triglyceride and carbohydrate glycogen and glucose stored within the body and there has been much research and practical experience over the past 30 y demonstrating the importance of muscle and liver glycogen for reducing fatigue and improving athletic performance.
Well-trained muscles store ____ percent more glycogen than untrained muscles. Carbohydrates are the most efficient fuel for working muscle and their contribution to total fuel oxidation is positively related to the intensity of exercise. As low to moderate-intensity exercise continues using aerobic metabolism fatty acids become the predominant fuel source for the exercising muscles.
During exercise we use a combination of these energy sources. Involves aerobic processing of carbohydrates to some extent with major utilization of protein. At the beginning of your aerobic workout your body converts carbohydrates into fuel.
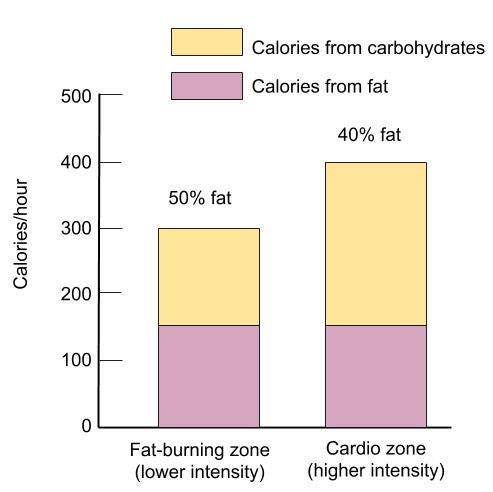
Helps fuel low- to moderate-intensity activityAt rest and during exercise performed at or below 65 percent of aerobic capacity fat contributes 50 percent or more of the fuel that muscles need. At mild-moderate exercise levels the percentage contribution from carbs and fat is the same whether the legs or the arms are exercising. Fat is the dominant energy source at low aerobic power outputs 40 VO 2 max and provides 50 of the required energy during moderate intensity exercise 40-65 VO 2 max.
At a high-intensity the primary energy source is the carbohydrate and at a low-intensity fat is the predominant source. The exercise intensity determines the contribution of the type of fuel source used for ATP productionsee Figure 164 The Effect of Exercise Intensity on Fuel Sources. In fact most people dont realize that even during light to moderate exercise carbohydrates can provide up to 40 to 60 percent of the total energy requirements.
Maximizing glycogen stores before an endurance event by diet and training. As you transition from low- to moderate-intensity exercise you begin to use a higher percentage of carbohydrate-based energy sources. In most people carbohydrate fuels approximately 90 seconds of activity.
Fuel Sources For Exercise Nutrition Science And Everyday Application

Fluent Rehabilitated Clean Bulk Diet Try It Today Lean Eating Healthy Carbs Diet And Nutrition

Pin On Alzheimers Dementia Products

Microorganisms As Bioindicators Of Water Pollution Activity Ms Ess3 3 46 Images Pollution Activities Middle School Science High School Science
Exercise Energy Systems A Primer
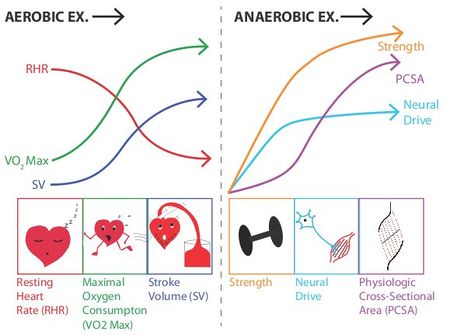
Anaerobic Exercise Physiopedia

Career And Social Media On Instagram Professionalism In The Workplace Source Theunderrecruiter Com Professionalism In The Workplace Workplace Interpersonal
Fuel Sources For Exercise Nutrition Science And Everyday Application

Order Of The Planets Mnemonic Device Mnemonic Devices Planet Order Mnemonics
Fuel Sources For Exercise Nutrition Science And Everyday Application

Inexpensive And Thoughtful Graduation Gifts For Students The Creative Classroom By Teachers Student Gifts High School Graduation Gifts Senior Gifts
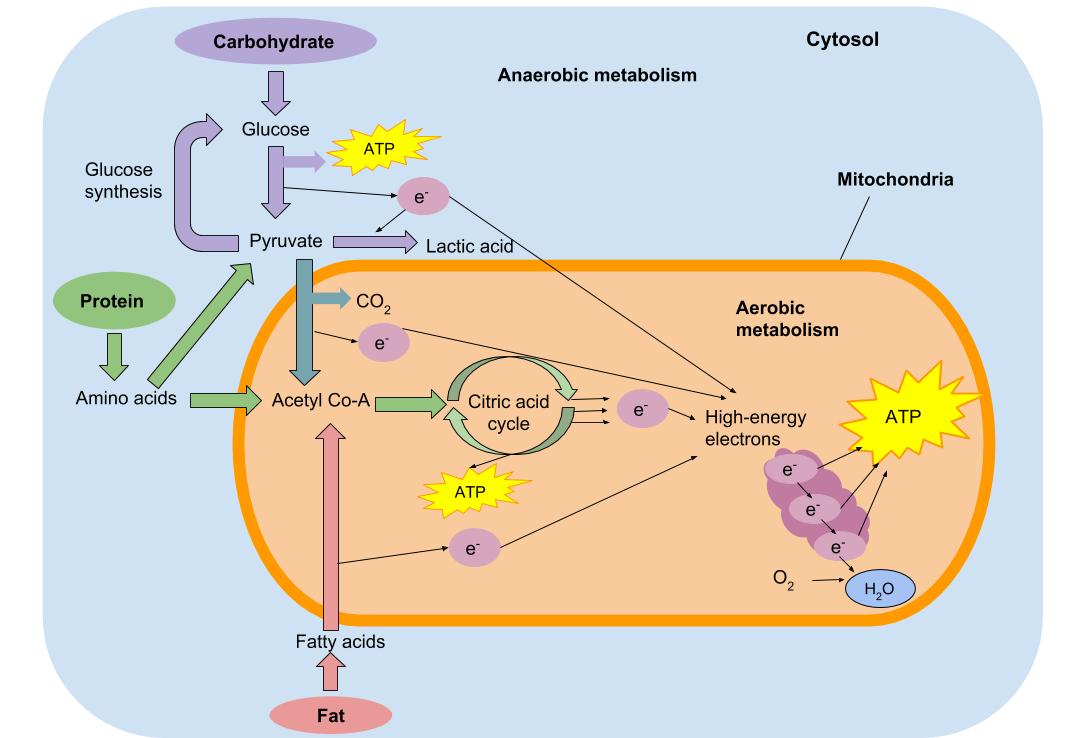
Fuel Sources For Exercise Nutrition Science And Everyday Application

Fuel Sources For Exercise Nutrition Science And Everyday Application
Fuel Sources Human Nutrition Deprecated

275 California Drought Maps Show Deep Drought And Recovery California Drought Drought California





Comments
Post a Comment